Blockchain Explained: How It Powers Crypto, DeFi, and Digital Assets
When you hear blockchain, a distributed digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that records can’t be altered retroactively. Also known as distributed ledger technology, it’s the foundation that makes Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of other crypto projects possible. It’s not magic. It’s not just a database. It’s a system designed to remove middlemen—banks, brokers, clearinghouses—and let people transact directly, securely, and transparently.
Behind every proof-of-stake, a consensus mechanism where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on how much cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral network like Ethereum or Cardano, there’s a blockchain keeping track of who owns what. And every time you interact with a smart contract, a self-executing code on a blockchain that runs when predefined conditions are met—like claiming an airdrop, swapping tokens on a decentralized exchange, or staking your coins—you’re using that blockchain. These aren’t theoretical ideas. They’re running right now, handling billions in value, often without any company or person in charge.
Blockchains don’t just store money. They store identity, ownership, rules, and even games. That’s why you see them in NFT marketplaces, crypto exchanges like xExchange and Nimera, and DeFi protocols like STBL that use real-world assets to generate yield. They’re also why countries like China ban them outright—because they can’t control what happens on a decentralized network. And when the SEC fines crypto firms billions, it’s because they’re trying to apply old financial rules to a system built to operate outside them.
Some blockchains are slow and expensive. Others are fast, cheap, and private. Some let anyone join. Others are locked down by governments or corporations. But they all share the same core idea: trust without a middleman. That’s why understanding blockchain isn’t about learning how to mine or code. It’s about knowing what’s possible when systems don’t need permission to work.
Below, you’ll find real-world breakdowns of how blockchain affects everything from your wallet security to global banking rules. No fluff. No hype. Just what’s actually happening on the chain—and what you need to know to protect your assets, spot scams, and make smarter moves in Web3.
1 Mar
2026
The genesis block is the first block in any blockchain, setting the foundation for all transactions and rules. Created in 2009 for Bitcoin, it's immutable, hardcoded, and carries symbolic meaning. Every crypto network relies on it to establish trust.
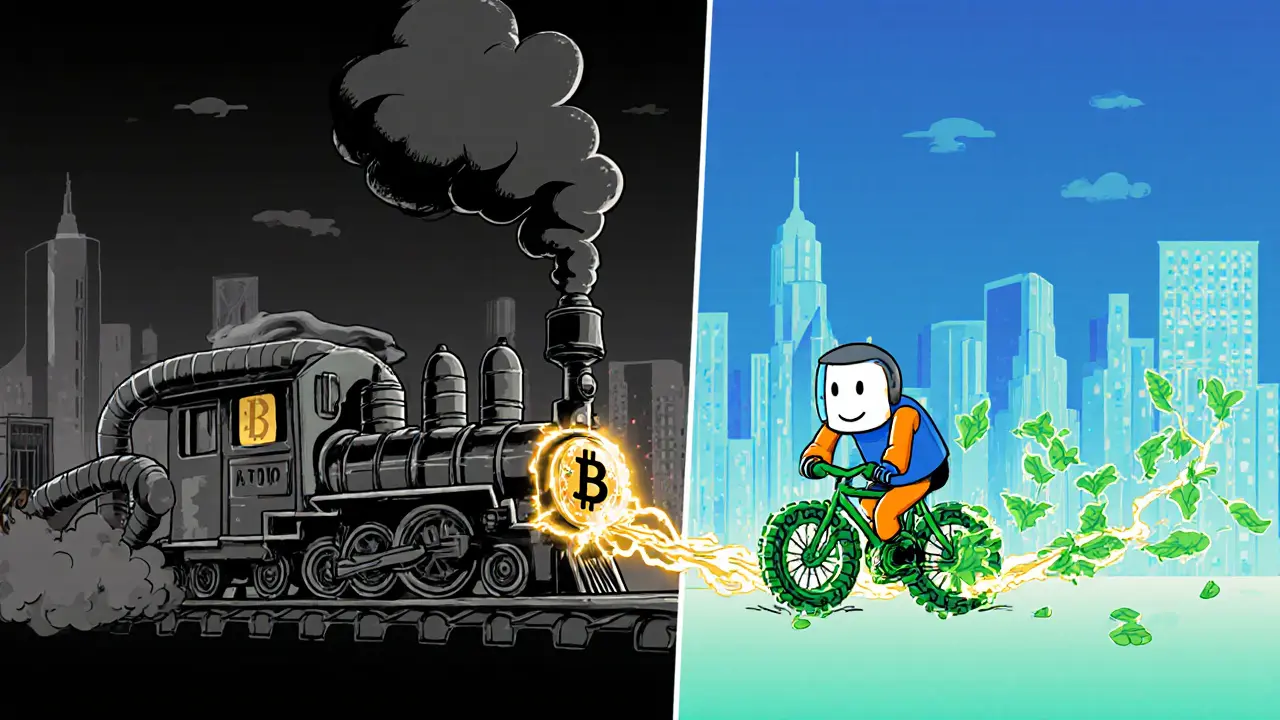
Proof of Stake slashed blockchain energy use by 99.95% when Ethereum switched in 2022. Discover how PoS works, why it's greener than Bitcoin, and why every new blockchain is choosing it.
Proof of Stake uses 99.95% less energy than Proof of Work, making it the most sustainable blockchain consensus model. Ethereum's 2022 switch slashed its power use from gigawatts to megawatts, setting a new standard for the industry.